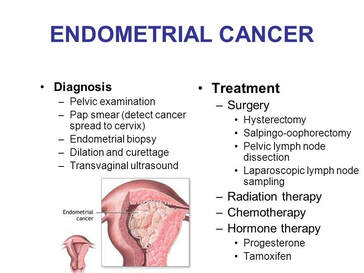
 Uterine Cancer is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers among women. This type of cancer starts in the lining of the womb, the endometrial tissue. This form is also known as endometrial polyps. The symptoms for uterine cancer usually include. Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge with a foul smell. Difficulty urinating, problems with sexual intercourse and infertility. There are many risk factors that can be developed by a woman who has developed uterine cancer. A family history of this disease is the number one risk factor. Other risk factors include being a smoker, having multiple sex partners and age over 50. A woman who has had cancer before is at greater risk to develop it again. Weight gain, diabetes, being obese, lack of exercise and recent surgery to the reproductive organs can also increase the risk of developing this disease. All of these risk factors can be controlled and managed, if you have been tested for this disease. One treatment option that is often used to treat uterine cancer is surgery. Surgery is often used when the cancer has spread. During a surgery called a hysterectomy, the doctor will remove the uterus and cervix. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted drug therapy is sometimes used. Treatment options depend on what stage the uterine cancer is at how big it is and whether or not it has spread to other parts of the body. In most cases, the early-stage cancers are treated with surgery, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted drugs like gemcitabine and tamoxifen. Once the tumors have spread, the more advanced treatments are used. Women who have uterine cancer that has not spread to the other parts of the body but has begun showing symptoms, may be given a hysterectomy and hormone therapy. The doctor may also decide to treat the tumor with radiation therapy. Other women in this situation may need surgery only. Her medical history and her endocrine profile can help determine the best course of treatment for this condition. A woman should always go into a physical examination by her physician with any of the following signs: irregular menstrual periods, pain in the lower abdomen, bladder or bowel incontinence, rectal bleeding, abdominal swelling or tenderness, and a feeling of fullness in the pelvic region. These signs indicate that a woman has a high risk for uterine cancer. If a woman has one or more of these signs, she should be seen by a doctor as soon as possible for proper evaluation. Women should never get stressed out about having a Pap smear or a pelvic exam. These tests are important and will allow your doctor to diagnose you if you have uterine cancer. Vaginal bleeding is very common in pre-menopausal women, usually associated with peri-menopause and often accompanied by vaginal spotting. When a woman goes through peri-menopause, there are many hormonal changes that take place in the body. A daily, monthly or yearly Pap smear will help your doctor to detect changes in your reproductive health. Abnormal vaginal bleeding is also a sign of uterine cancer and should be checked out. The most common surgical procedure for treating this disease is called a hysterectomy. This procedure removes the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and cervix. Sometimes the doctor will also remove the surrounding tissue around the uterus, such as the pelvic lymph nodes. There are several reasons why a woman would want to undergo a hysterectomy. If your cancer has spread (metastasized) to other areas of your body, a hysterectomy may be your only option. A hysterectomy can also be recommended if you are past menopause and have lost your ability to produce hormones. This is the most common type of surgery for uterine cancer and occurs when the cancer has spread to other parts of your body. Another reason a doctor might recommend a hysterectomy is if your cancer has spread to your bladder and/or kidneys. In this case, the removal of your uterus is not needed. Other procedures may be needed to remove the affected areas. The treatment options for uterine cancer vary depending on which type of cancer is detected. This includes surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and alternative treatments, like acupuncture and different types of medicine. Surgery for uterine cancer is performed in two ways: either an open or laparoscopic procedure. With the use of a laparoscope, a thin tube is placed into the uterus. Another option to treat uterine cancer is with internal radiation therapy. This option involves sending radiation through the abdomen, pelvis, and ribs. Internal radiation therapy uses the same equipment that is used to treat external cancers with radiation, only it is directed inside the body. The increased dose of radiation damages cancer cells and helps to shrink tumors while shrinking the size of benign tumors.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
July 2024
AuthorSteve Schafer is the founder of TheEulogyWriters and the author of hundreds of heartfelt, wonderful eulogies. He lives in Texas and has been writing eulogies for well over thirty years. The articles in this blog are designed to help people through the process of losing loved ones and exploring issues in the aging process. |
|
The Eulogy Writers
4092 Old Dominion Dr. West Bloomfield, MI 48323 |
Writers: Steve Schafer, Ralph DiBiasio-Snyder, Abi Galeas, Miriam Hill
Steve's Personal Cell Phone: (734) 846-3072 Our email address is: [email protected] |