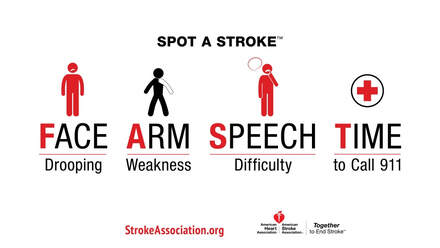
 Stroke is the third largest cause of mortality worldwide. Stroke, which is also known as ischemic stroke, accounts for more than half of all stroke deaths. Stroke can affect any part of the human body but the most common locations are the brain and the spinal cord. If you suffer from stroke you will experience certain symptoms. Symptoms of a stroke depend on the type of stroke and can include loss of consciousness, paralysis, dizziness, impaired thinking, ringing in the ears, and sudden numbness or tingling in the extremities. The majority of stroke victims experience both signs and symptoms, but some suffer only one or the other. The most important treatment for stroke is ongoing care after stroke to reduce disability and improve the function of the affected body parts. An increasing number of patients who have suffered a stroke require surgery to remove part of the cerebrospinal fluid (the space inside the brain and spinal cord) to improve or restore brain function. This surgery is called a stroke rehab and usually follows a mild stroke. Successful rehabilitation will increase blood flow to the injured areas, resulting in improvement or complete recovery. Less frequent but more serious strokes are caused by hemorrhaging or bleeding of the internal brain arteries, which supply blood to the different parts of the brain. Hemorrhaging typically occurs in patients who have had a previous stroke or heart attack. When this occurs, less blood flows to the brain causing decreased brain functions. The damaged or degenerated blood clot in the artery can form a clot in the blood stream and prevent the proper flow of oxygen-rich blood to brain cells, damaging them and making it impossible for them to function normally. To prevent this condition from occurring, it is important that the clots are cleared or dissolved by means of a specialized procedure before they begin to form. There are several different types of medications that are used for this purpose. One type of drug, done by injection, prevents the formation of a blood clot on the vessel wall, thus reducing the amount of bleeding. Another, called angiotensin Receptors Inhibitors, prevents or breaks up the protein compound that is responsible for the formation of blood clots. A less common type of blockage of a blood vessel is called Lacunar stroke. It results when the brain tissue is damaged inside a blood vessel, usually in the neck or head. As with hemorrhaging, Lacunar stroke requires medication to break up the clotted blood. Again, the most successful method of treatment is prevention. Hypertension, a predisposition to high blood pressure, is often considered a silent stroke. It does increase the risk factor, but those who already have hypertension do not necessarily contract it. The most recent study to look at this question discovered that hypertensive patients were at twice the risk of having a stroke than non-hypertensive people. This particular stroke-causing factor, however, should be taken into consideration if hypertension is an issue in one's life - especially if other risk factors (such as high blood pressure) exist and are well known. Any one of these symptoms can indicate the presence of a stroke - although having more than one can indicate a greater likelihood of having serious complications. If someone has had symptoms and has been able to get treatment, doctors know how to best treat the symptoms and the person as a whole. If someone doesn't get the treatment they need, however, strokes may occur, and the effects can be deadly. Symptoms that suggest a stroke may be imminent include lethargy, problems with movement or speech, loss of coordination, dizziness, and slurred speech. Weakness on one side of the body is also a sign of potential problems. Stroke symptoms can include a wobble in the hearing abilities or trouble with communication. Some patients with mild stroke may also exhibit flu-like symptoms such as fatigue or depression. A patient with weak muscles or paralysis of one side of the body is also more likely to suffer from a stroke. A very serious condition, transient ischemic attack, also called TIA, can occur after the onset of a stroke. Having symptoms such as: a pounding heart, dizziness, nausea, or trouble breathing require immediate medical attention. If you are experiencing any or all of these symptoms, call 911 immediately. The sooner that you are able to reach the emergency room, the sooner your chances for survival increase dramatically. Because there are many different forms of stroke, it is important that you seek treatment to address your specific symptoms. These symptoms can range from the mild to the more severe and can even be confusing and debilitating for those who experience them. Understanding how they are caused and your options for treatment will be the key to regaining your independence and feeling stronger. If you experience any or all of the symptoms of stroke mentioned in this article, make sure to contact your physician so he or she can assess your condition and determine the best course of treatment.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
July 2024
AuthorSteve Schafer is the founder of TheEulogyWriters and the author of hundreds of heartfelt, wonderful eulogies. He lives in Texas and has been writing eulogies for well over thirty years. The articles in this blog are designed to help people through the process of losing loved ones and exploring issues in the aging process. |
|
The Eulogy Writers
4092 Old Dominion Dr. West Bloomfield, MI 48323 |
Writers: Steve Schafer, Ralph DiBiasio-Snyder, Abi Galeas, Miriam Hill
Steve's Personal Cell Phone: (734) 846-3072 Our email address is: [email protected] |