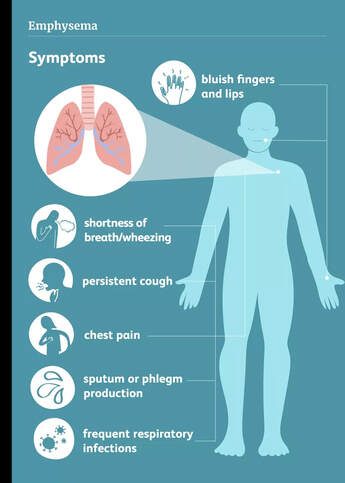
 Pulmonary disease (CP) is a condition that can affect anyone. It is a disease that damages the airways, the tubes that transport air in and out of the lungs. When this occurs, the airways become narrowed or blocked, causing problems with breathing. These problems can include shortness of breath or even pneumonia. COPD is the most common type of chronic pulmonary disease and accounts for about 80 percent of all cases. There are different types of CPP, but the most common are two. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, also known as COPD, is an inflammation of the airways. The disease has a few traits which have to be present in order to be diagnosed correctly: persistent coughing that doesn't go away, produces thick mucus or phlegm regularly, and lasts more than three months in a consecutive year. This symptom usually gets worse overtime. Emphysema is a more severe form of COPD and involves permanent damage to the air sacs of the lungs. This makes it impossible for the lungs to retain air and leads to breathing problems. The causes of Emphysema are related to the development of scar tissue and narrowing of the air sacs in the lungs. One of the most common treatments for this condition is continuous positive air pressure or CPAP, which helps maintain the air sacs at their normal sizes. Two other treatments are used in a limited number of patients: alveolar air sac replacement therapy, which uses an artificial sphincter to close the air sacs and assist with breathing; and supplementary oxygen therapy or SOT, which utilizes a gas supply that helps replace the lost oxygen in the tissues. Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition where the lining of the lungs becomes thick and scarred. In certain cases, smoking is a known cause. There are other treatments for this condition, however, including a therapy called pulsatile or edentulous xenon saturation therapy. Smokers who use this treatment have shown to stop smoking by more than 60%. In addition to these treatments, people who suffer from this condition may also need to stop taking their regular medications such as inhalers, compression stockings, and nebulizers. One more serious condition is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD, which can result from many factors such as smoking, chronic exposure to chemicals, or viral infections. A person with COPD may be having difficulty breathing every minute of the day. In addition, they may cough up bloody mucus. On top of this, there's always the chance that their condition will worsen if they don't do anything about it, so they need to have an accurate prediction of how their condition will progress in the future. The symptoms of COPD include chronic coughing or asthma-like symptoms that are present in the early stages of the disease. Other signs that will indicate that you're suffering from COPD include shortness of breath and chest pain. Shortness of breath occurs when the person isn't taking in enough oxygen. Chest pain happens when the airway is narrowed or blocked, making it hard for the person to take in enough oxygen. Although shortness of breath and chest pain are the most common symptoms, you may also start to feel fatigued or exhausted. The main complications associated with COPD include infection of the lungs and increased risks of heart attack, stroke, and diabetes. Cigarette smoke irritates the lining of the lungs and causes shortness of breath and increased coughing. This irritates the airways by thinning them and obstructing them, which increases congestion and decreases oxygen flow. Over time, with long-term cigarette smoking, irritants can lead to serious health problems and inflammation in the lining of the lungs. Other complications of COPD include sleep apnea and pneumonia. Chronic bronchial asthma makes it difficult to breathe. People who have this type of disease are advised to take in lots of fresh air and exercise frequently. Cigarette fumes and other environmental factors cause irritants to become airborne and reach your bloodstream, where they attach themselves to proteins and DNA molecules. When the body cannot absorb the toxins, the liver produces more mucous in an attempt to expel the toxins. The result is excess mucous that can build up in the lungs and cause shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and discomfort. COPD symptoms are very similar to those of chronic bronchitis, the leading cause of death in people with this disease.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
July 2024
AuthorSteve Schafer is the founder of TheEulogyWriters and the author of hundreds of heartfelt, wonderful eulogies. He lives in Texas and has been writing eulogies for well over thirty years. The articles in this blog are designed to help people through the process of losing loved ones and exploring issues in the aging process. |
|
The Eulogy Writers
4092 Old Dominion Dr. West Bloomfield, MI 48323 |
Writers: Steve Schafer, Ralph DiBiasio-Snyder, Abi Galeas, Miriam Hill
Steve's Personal Cell Phone: (734) 846-3072 Our email address is: [email protected] |